2.4. Growth Rates Review¶
2.4.1. Growth Rates Review¶
Two functions of \(n\) have different growth rates if, as \(n\) goes to infinity, their ratio either goes to infinity or goes to zero.
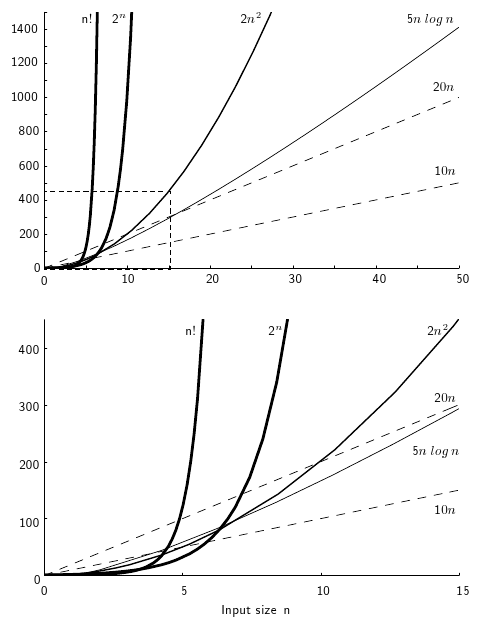
Figure 2.4.1: Two views of a graph illustrating the growth rates for six equations. The bottom view shows in detail the lower-left portion of the top view. The horizontal axis represents input size. The vertical axis can represent time, space, or any other measure of cost.¶
Where would the line for the equation \((1.618)^n\) go on this graph?
Exact equations relating program operations to running time require machine-dependent constants. Sometimes, the equation for exact running time is complicated to compute. Usually, we are satisfied with knowing an approximate growth rate. Specifically, we don’t generally care about the contants in the equations. Given two algorithms with growth rate \(c_1n\) and \(c_2 2^{n!}\), do we need to know the values of \(c_1\) and \(c_2\)?
Here are some useful observations.
Since \(n^2\) grows faster than \(n\),
\(2^{n^2}\) grows faster than \(2^n\). (Take antilog of both sides.)
\(n^4\) grows faster than \(n^2\). (Square boths sides.)
\(n\) grows faster than \(\sqrt{n}\). (\(n = (\sqrt{n})^2\). Replace \(n\) with \(\sqrt{n}\).)
\(2 \log n\) grows no slower than \(\log n\). (Take \(\log\) of both sides. Log “flattens” growth rates.)
Since \(n!\) grows faster than \(2^n\),
\(n!!\) grows faster than \(2^n!\). (Apply factorial to both sides.)
\(2^{n!}\) grows faster than \(2^{2^n}\). (Take antilog of both sides.)
\(n!^2\) grows faster than \(2^{2n}\). (Square both sides.)
\(\sqrt{n!}\) grows faster than \(\sqrt{2^n}\). (Take square root of both sides.)
\(\log n!\) grows no slower than \(n\). (Take log of both sides. Actually, it grows faster since \(\log n! = \Theta(n \log n)\).)
If \(f\) grows faster than \(g\), then must \(\sqrt{f}\) grow faster than \(\sqrt{g}\)? Yes.
Must \(\log f\) grow faster than \(\log g\)? No. \(\log n \approx \log n^2\) within a constant factor, that is, the growth rate is the same! Again, the log operator “flattens” the relative growth rates.
\(\log n\) is related to \(n\) in exactly the same way that \(n\) is related to \(2^n\).
\(2^{\log n} = n\).
2.4.1.1. Asymptotic Notation¶
The notation “\(f \in O(n^2)\)” is preferred to “\(f = O(n^2)\)”. While \(n \in O(n^2)\) and \(n^2 \in O(n^2)\), \(O(n) \neq O(n^2)\).
Note that Big oh does not say how good an algorithm is—only how bad it can be.
If algorithm \(\mathcal{A}\in O(n)\) and algorithm \(\mathcal{B} \in O(n^2)\), is \(\mathcal{A}\) better than \(\mathcal{B}\)? Perhaps… but perhaps the problem is that we don’t know much about the analysis of these algorithms. Perhaps better analysis will show that \(\mathcal{A} = \Theta(n)\) while \(\mathcal{B} = \Theta(\log n)\).
Some log notation: \(\log n^2 (= 2 \log n)\) vs. \(\log^2 n (= (\log n)^2)\) vs. \(\log \log n\).
\(\log 16^2 = 2 \log 16 = 8\).
\(\log^2 16 = 4^2 = 16\).
\(\log \log 16 = \log 4 = 2\).
Order Notation has practical limits. Consider this statement: Resource requirements for Algorithm \(\mathcal{A}\) grow slower than resource requirements for Algorithm \(\mathcal{B}\). Is \(\mathcal{A}\) better than \(\mathcal{B}\)? There are some potential problems with claiming so.
How big must the input be before it becomes true?
Some growth rate differences are trivial. For example: \(\Theta(\log^2 n)\) vs. \(\Theta(n^{1/10})\). If \(n\) is \(10^{12} (\approx 2^{40})\) then \(\log^2 n \approx 1600\), \(n^{1/10} = 16\) even though \(n^{1/10}\) grows faster than \(\log^2 n\). \(n\) must be enormous (like \(2^{150}\)) for \(n^{1/10}\) to be bigger than \(\log^2 n\).
It is not always practical to reduce an algorithm’s growth rate. “Practical” here means that the constants might become too much higher when we shave off the minor asymptotic growth. Shaving a factor of \(n\) reduces cost by a factor of a million for input size of a million. Shaving a factor of \(\log \log n\) saves only a factor of 4-5. So if changing the algorithm to remove a factor of \(\log \log n\) at the expense of a constant factor of 10, then the new algorithm (while asymptotically better) won’t realize its advantages until \(n\) is so big as to never be used in any real situation.
This leads to the concept of the practicality window. In general, (1) we have limited time to solve a problem, and (2) input can only get so big before the computer chokes (or at least, users are only interested in running problems of a certain size). So while one algorithm might be asymptotically better than another, perhaps this is not true within the range of practical inputs that the user actually would require.
Fortunately, algorithm growth rates are USUALLY well behaved, so that Order Notation gives practical indications. “Practical” is the keyword. We use asymptotics because they provide a simple model that usually mirrors reality. This is useful to simplify our thinking.


