6.1. General Trees¶
6.1.1. General Trees¶
6.1.1.1. General Trees¶
6.1.1.2. General Tree ADT¶
// General tree node ADT public interface GTNode { public Object value(); public boolean isLeaf(); public GTNode parent(); public GTNode leftmostChild(); public GTNode rightSibling(); public void setValue(Object value); public void setParent(GTNode par); public void insertFirst(GTNode n); public void insertNext(GTNode n); public void removeFirst(); public void removeNext(); } // General tree ADT public interface GenTree { public void clear(); // Clear the tree public GTNode root(); // Return the root // Make the tree have a new root, give first child and sib public void newroot(Object value, GTNode first, GTNode sib); public void newleftchild(E value); // Add left child }
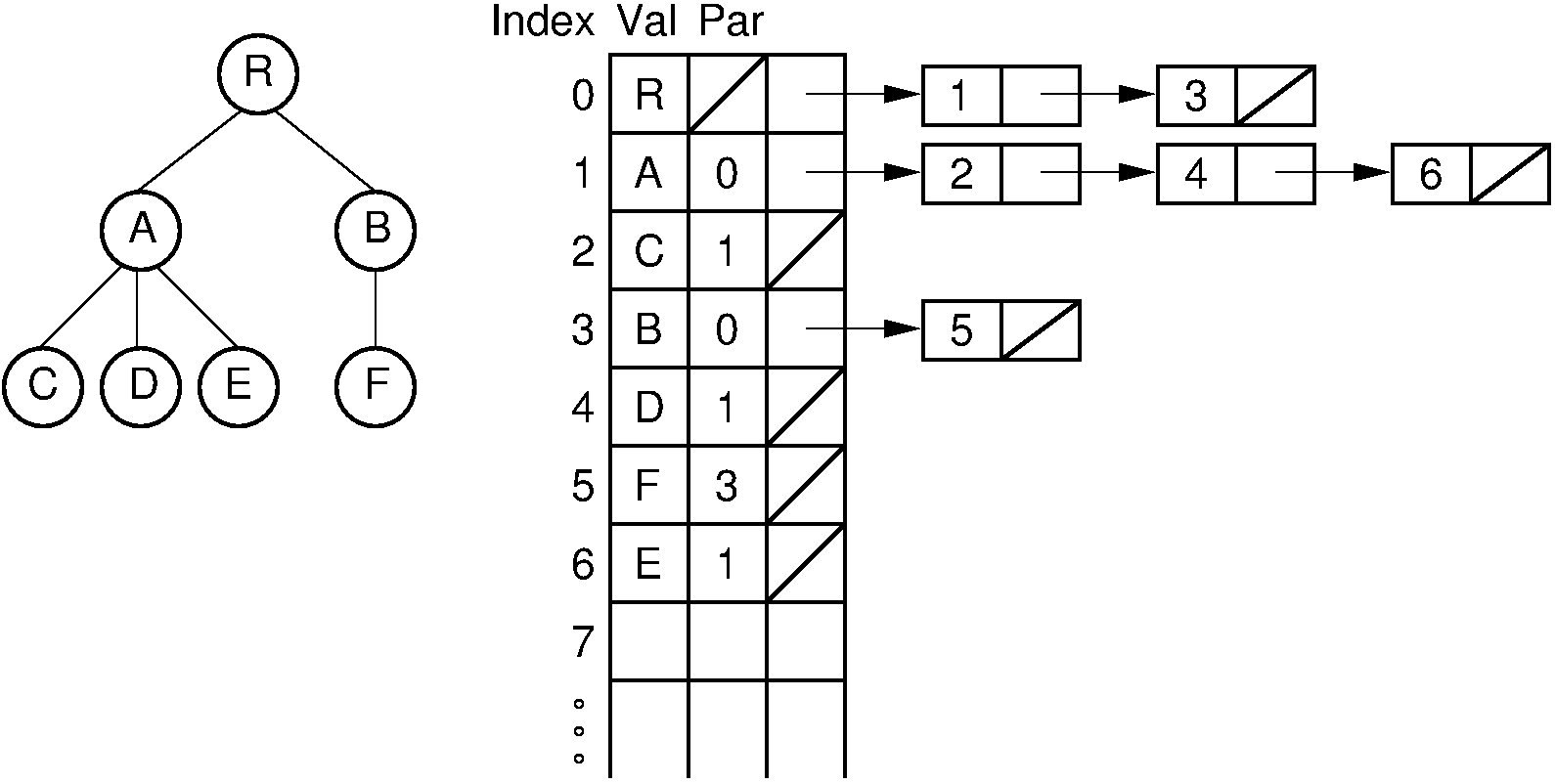
6.1.1.4. Rep: Lists of Children¶
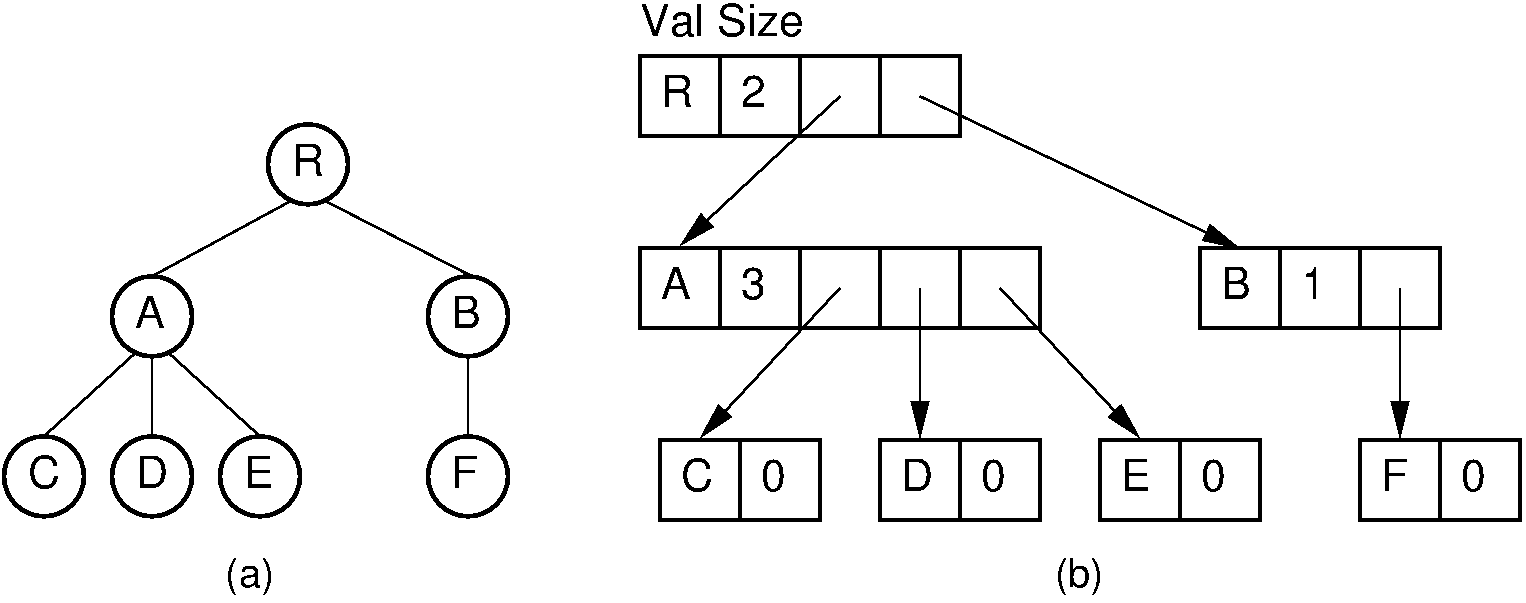
6.1.1.5. Rep: Dynamic Node (Array)¶
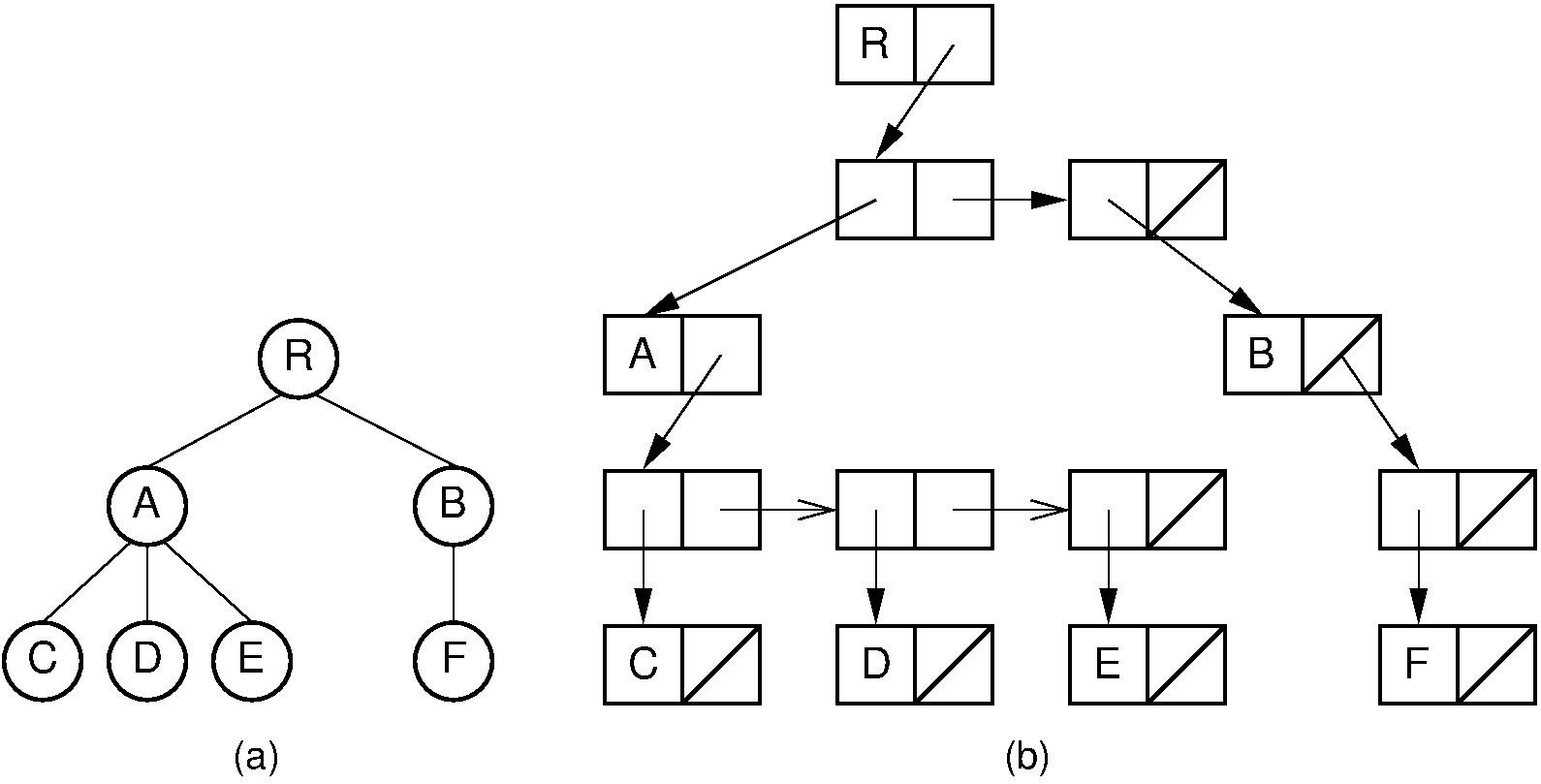
6.1.1.6. Rep: Dynamic Node (linked list)¶
6.1.1.7. Rep: Lift-Child/Right-Sibling¶
6.1.1.8. Serialization¶
Serialization is the process of storing an object as a series of bytes.
A sequential tree serialization typically stores the node values as they would be enumerated by a preorder traversal, along with sufficient information to describe the tree’s shape.