12.15. A Hard Information Flow Problem¶
Sometimes, passing the right information up and down the tree to control a recursive function gets complicated. The information flow itself is simple enough, but deciding what to pass might be tricky. Here is an example with checking to see if a given binary tree follows the rules for a BST.
Example 12.15.1
A more difficult example is illustrated by the following problem. Given an arbitrary binary tree we wish to determine if, for every node \(A\), are all nodes in \(A\)'s left subtree less than the value of \(A\), and are all nodes in \(A\)'s right subtree greater than the value of \(A\)? (This happens to be the definition for a binary search tree.) Unfortunately, to make this decision we need to know some context that is not available just by looking at the node's parent or children.
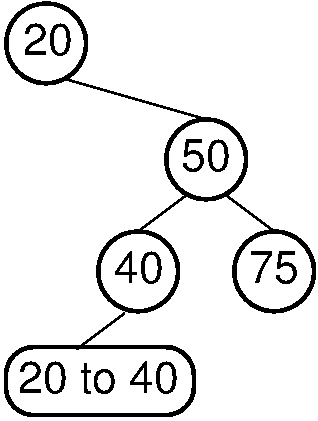
Figure 12.15.1: To be a binary search tree, the left child of the node with value 40 must have a value between 20 and 40.
As shown by Figure , it is not enough to verify that \(A\)'s left child has a value less than that of \(A\), and that \(A\)'s right child has a greater value. Nor is it enough to verify that \(A\) has a value consistent with that of its parent. In fact, we need to know information about what range of values is legal for a given node. That information might come from any of the node's ancestors. Thus, relevant range information must be passed down the tree. We can implement this function as follows.


